Neo Malthusian Theory: Understanding Its Impact on Population and Resources?
Introduction
Neo Malthusian theory is an extension of the ideas first proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus in his 1798 work, An Essay on the Principle of Population. This modern adaptation warns about the dangers of overpopulation, emphasizing the depletion of resources, environmental degradation, and the necessity for proactive population control. With global concerns about sustainability, climate change, and food security, Neo-Malthusianism remains highly relevant. This article explores the core principles, historical background, criticisms, and contemporary significance of Neo Malthusian theory.
What is Neo Malthusian theory?
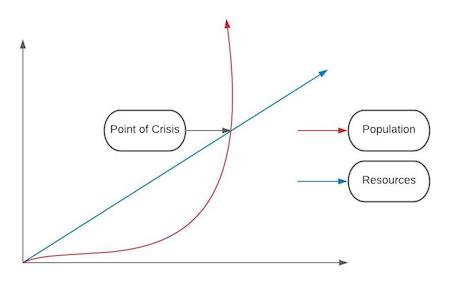
Neo Malthusian theory builds upon Malthus’s original argument that population growth outpaces food production, leading to shortages and societal crises. However, Neo-Malthusians extend this concern beyond food supply to issues like water scarcity, climate change, deforestation, and pollution. The theory advocates for measures such as contraception, family planning, and sustainable development to curb excessive population growth.
Historical Background
Malthus’s original theory suggested that human population grows geometrically while food production increases arithmetically. This imbalance, he argued, would result in famine, war, and disease unless checked by factors like moral restraint or natural disasters.
Neo-Malthusian thought gained traction in the 20th century, particularly with the publication of Paul R. Ehrlich’s The Population Bomb in 1968. Ehrlich predicted that unchecked population growth would lead to global famine and resource depletion. Similarly, the Club of Rome’s 1972 report The Limits to Growth reinforced concerns about finite resources, predicting economic collapse due to overconsumption.
Key Principles of Neo-Malthusianism
- Population Control: Neo-Malthusians argue that high population growth leads to resource exhaustion and environmental destruction. They advocate for birth control, education, and government policies to limit fertility rates.
- Resource Scarcity: The theory warns that the Earth’s resources are finite, and excessive consumption can lead to shortages of food, water, and energy.
- Environmental Concerns: Overpopulation is linked to deforestation, climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
- Technological Skepticism: While some believe technological advancements can offset resource scarcity, Neo-Malthusians remain cautious, arguing that innovation alone cannot solve overpopulation’s challenges.
Criticisms of Neo Malthusian theory
Despite its influence, Neo-Malthusianism has faced substantial criticism:
- Technological Advancements: Critics argue that agricultural innovations, such as the Green Revolution, have increased food production, disproving Malthus’s prediction of mass starvation.
- Economic Perspectives: Scholars like Julian Simon have argued that human ingenuity and market forces can address resource scarcity through adaptation and efficiency.
- Ethical Concerns: Some argue that population control measures, particularly coercive policies like China’s one-child policy, violate human rights.
- Demographic Transition Theory: This theory suggests that as societies develop, birth rates naturally decline, making forced population control unnecessary.
Modern Relevance of Neo Malthusian theory
Despite criticisms, the principles of Neo-Malthusianism remain significant in today’s world. Issues like climate change, overconsumption, and rapid urbanization align with its predictions. Some contemporary concerns include:
- Climate Change: Rising global temperatures and extreme weather patterns are exacerbated by high population density and resource consumption.
- Water Scarcity: Overpopulation leads to increased water demand, causing shortages in many regions.
- Food Security: While technology has improved food production, inequitable distribution still results in hunger and malnutrition.
- Urban Overcrowding: Rapid population growth has led to housing crises, traffic congestion, and strained public services in megacities.
Conclusion
Neo Malthusian theory continues to shape discussions on sustainability, resource management, and environmental policies. While technological progress has addressed some concerns, population growth and consumption patterns remain critical challenges. Finding a balance between economic development and environmental preservation is essential for a sustainable future. Whether one supports or criticizes Neo-Malthusianism, its warnings about resource limitations and overpopulation remain relevant in the modern world.
You may also read: Which Helps Enable an Oligopoly to Form Within a Market?